
원문 : https://javascript.plainenglish.io/10-must-know-javascript-tricks-tips-about-reduce-1368766d99da
코드를 덜 작성하고 더 많은 일을 하게 만드는 Reduce에 대한 10가지 트릭
프론트엔드 개발자로써 reduce 함수는 반드시 많이 사용해야하고, 강력하고 유용한 배열(array) API입니다. 오늘은 이에 대한 10가지 고급 트릭과 팁을 공유하고자 합니다.
1. 가산기 및 누산기
"reduce"를 사용하면 여러 숫자들을 더하거나 누적하는 기능을 쉽게 구현할 수 있습니다.
// 가산기
const sum = (...nums) => {
return nums.reduce((sum, num) => sum + num);
};
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 10)); // 20
// 누산기
const accumulator = (...nums) => {
return nums.reduce((acc, num) => acc * num);
};
console.log(accumulator(1, 2, 3)); // 6
2. 배열의 최대값과 최소값 계산
배열의 최대값 또는 최소값을 구하는 방법은 무엇이 있을까요?
1: Math.max 및 Math.min 사용
Math API를 사용하는 것이 가장 쉬운 방법이라는 것을 인정해야 합니다.
const array = [-1, 10, 6, 5];
const max = Math.max(...array); // 10
const min = Math.min(...array); // -1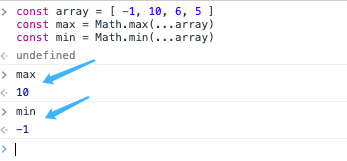
2: reduce 사용
한 줄의 코드로 Math의 API와 동일한 효과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
const array = [-1, 10, 6, 5];
const max = array.reduce((max, num) => (max > num ? max : num));
const min = array.reduce((min, num) => (min < num ? min : num));
3. 검색 파라미터 포맷
링크에서 검색 파라미터를 얻어야 하는 경우가 종종 있습니다. 어떻게 파싱하면 좋을까요?
예시
// url https://qianlongo.github.io/vue-demos/dist/index.html?name=fatfish&age=100#/home
// 검색 파라미터 포맷
{
"name": "fatfish",
"age": "100"
}1. 일반적인 방법
이것이 대부분의 사람들이 사용하는 방식입니다.
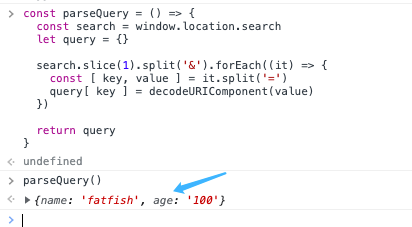
const parseQuery = () => {
const search = window.location.search;
let query = {};
search
.slice(1)
.split("&")
.forEach((it) => {
const [key, value] = it.split("=");
query[key] = decodeURIComponent(value);
});
return query;
};
2. reduce 사용
Reduce를 사용하여 더 간단하게 코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
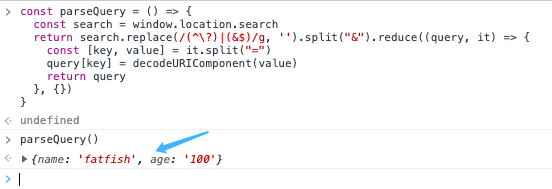
const parseQuery = () => {
const search = window.location.search;
return search
.replace(/(^\?)|(&$)/g, "")
.split("&")
.reduce((query, it) => {
const [key, value] = it.split("=");
query[key] = decodeURIComponent(value);
return query;
}, {});
};
어떻게 작동하나요?
// url https://qianlongo.github.io/vue-demos/dist/index.html?name=fatfish&age=100#/home
// 1. 첫 번째로 검색 파라미터를 얻습니다
const search = window.location.search; // ?name=fatfish&age=100
// 2. 시작에 "?" 또는 끝에 "&"를 제거합니다
search.replace(/(^\?)|(&$)/g, "");
// ?name=fatfish&age=100 => name=fatfish&age=100
// 3. 파라미터를 모으기 위해 reduce를 사용합니다
// ...4. 검색 파라미터 역직렬화
링크로 이동하여 검색 파라미터를 추가하려는 경우, 일일이 연결하는 방법은 그리 편리하지 않습니다.
연결해야 할 파라미터가 많으면 재앙이 됩니다.
const searchObj = {
name: "fatfish",
age: 100,
// ...
};
const link = `https://medium.com/?name=${searchObj.name}&age=${searchObj.age}`;
// https://medium.com/?name=fatfish&age=100다행히도 "reduce"는 이 문제를 쉽게 해결하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
const stringifySearch = (search = {}) => {
return Object.entries(search)
.reduce(
(t, v) => `${t}${v[0]}=${encodeURIComponent(v[1])}&`,
Object.keys(search).length ? "?" : ""
)
.replace(/&$/, "");
};
const search = stringifySearch({
name: "fatfish",
age: 100,
});
const link = `https://medium.com/${search}`;
console.log(link); // https://medium.com/?name=fatfish&age=100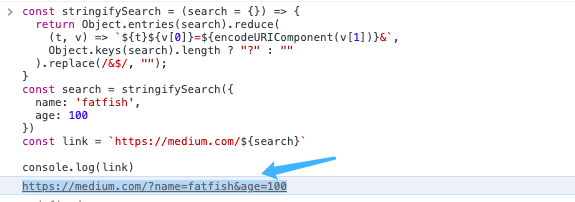
5. 다단계 중첩 배열 평탄화
다단계 중첩 배열을 평탄화하는 방법을 알고 있나요?
const array = [1, [2, [3, [4, [5]]]]];
// expected output [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
const flatArray = array.flat(Infinity); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]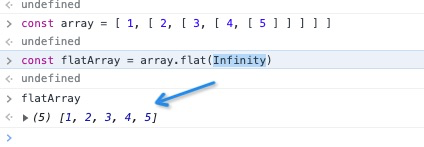
"flat"은 매우 강력한 API입니다. 자세한 내용을 보려면 여기를 클릭하세요.
reduce를 사용해도 flat과 동일한 기능을 하는 코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
const flat = (array) => {
return array.reduce(
(acc, it) => acc.concat(Array.isArray(it) ? flat(it) : it),
[]
);
};
const array = [1, [2, [3, [4, [5]]]]];
const flatArray = flat(array); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]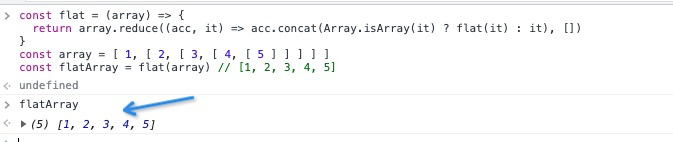
6. flat 기능 함수 시뮬레이션
깊이 중첩된 배열을 평탄화하는 기능을 구현했지만, 어떻게 flat 기능 전체를 구현하나요?
// 기본적으로 한 층을 이어 붙입니다
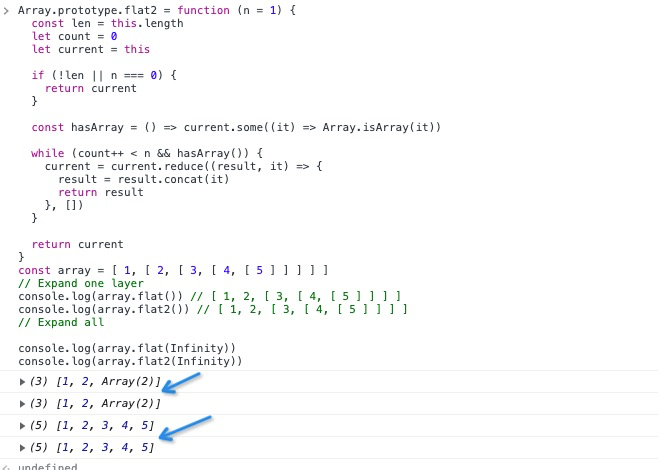
Array.prototype.flat2 = function (n = 1) {
const len = this.length;
let count = 0;
let current = this;
if (!len || n === 0) {
return current;
}
// 현재 배열 항목이 있는지 확인
const hasArray = () => current.some((it) => Array.isArray(it));
// 각 싸이클 후에 한 층을 이어 붙입니다
while (count++ < n && hasArray()) {
current = current.reduce((result, it) => {
result = result.concat(it);
return result;
}, []);
}
return current;
};
const array = [1, [2, [3, [4, [5]]]]];
// 한 층을 이어 붙입니다.
console.log(array.flat()); // [ 1, 2, [ 3, [ 4, [ 5 ] ] ] ]
console.log(array.flat2()); // [ 1, 2, [ 3, [ 4, [ 5 ] ] ] ]
// 모든 층을 이어 붙입니다.
console.log(array.flat(Infinity));
console.log(array.flat2(Infinity));우리가 해냈네요.
7. 배열을 고유하게 유지
reduce는 배열을 고유하게 유지하는 것도 쉽습니다.
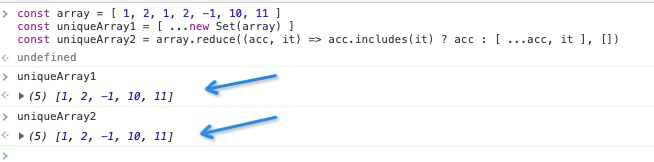
const array = [1, 2, 1, 2, -1, 10, 11];
const uniqueArray1 = [...new Set(array)];
const uniqueArray2 = array.reduce(
(acc, it) => (acc.includes(it) ? acc : [...acc, it]),
[]
);
8. 각 배열 요소의 갯수를 계산
배열 안에 있는 각 요소의 갯수를 계산하는 방법은 무엇일까요?
object 대신 Map을 사용하는 이유는 무엇일까요?
역주 : Map은 Object와는 다르게 삽입된 Key의 순서가 보장되기 때문입니다.
const count = (array) => {
return array.reduce(
(acc, it) => (acc.set(it, (acc.get(it) || 0) + 1), acc),
new Map()
);
};
const array = [1, 2, 1, 2, -1, 0, "0", 10, "10"];
console.log(count(array));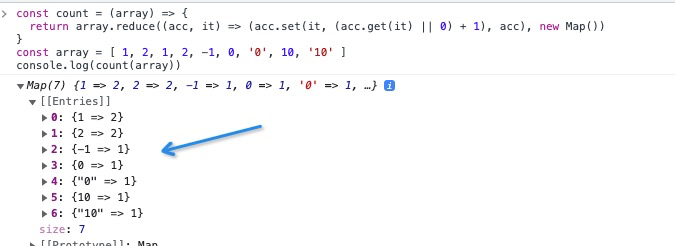
9. 객체의 여러 프로퍼티 가져오기
여러분이 업무 중에 마주하게 될 시나리오를 살펴보겠습니다.
// 많은 프로퍼티를 가진 객체가 있습니다.
const obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3,
d: 4,
e: 5,
// ...
};
// 새로운 객체를 만들고 그 위에 몇 가지 속성을 가져오고 싶습니다.
const newObj = {
a: obj.a,
b: obj.b,
c: obj.c,
d: obj.d,
// ...
};
// 이건 너무 비효율적이라고 생각하지 않나요?reduce를 사용해서 해결
const getObjectKeys = (obj = {}, keys = []) => {
return Object.keys(obj).reduce(
(acc, key) => (keys.includes(key) && (acc[key] = obj[key]), acc),
{}
);
};
const obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3,
d: 4,
e: 5,
// ...
};
const newObj = getObjectKeys(obj, ["a", "b", "c", "d"]);
console.log(newObj);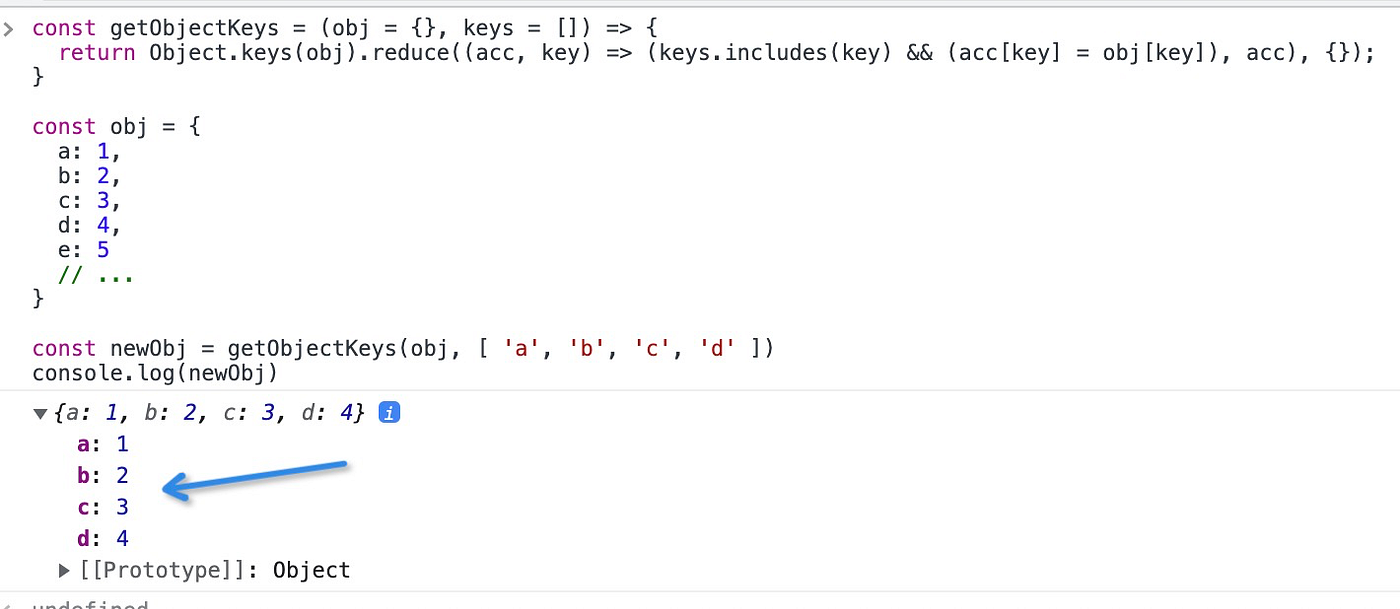
10. 문자열 반전
const reverseString = (string) => {
return string.split("").reduceRight((acc, s) => acc + s);
};
const string = "fatfish";
console.log(reverseString(string)); // hsiftaf마지막으로
읽어 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 글들을 더 많이 읽으실 수 있도록 팔로잉 부탁드립니다.
'아티클 번역' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [번역] JavaScript 패키지 매니저 비교 - npm, Yarn 또는 pnpm? (0) | 2022.12.11 |
|---|---|
| [번역] React에 SOLID 원칙 적용하기 (0) | 2022.12.11 |
| [번역] Remix: 리액트의 음에 양을 (1) | 2022.12.11 |
| [번역] Remixing React Router (0) | 2022.12.11 |
| [번역] 누구나 자바스크립트 제너레이터 함수가 필요한 이유는 무엇인가요? (0) | 2022.12.11 |
![[번역] Reduce에 대한 10가지 필수 JavaScript 트릭 및 팁](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FTHIvO%2FbtrThOmjI6V%2FiKLLZhh7OF0wBwPptdasM1%2Fimg.jpg)